Insights
Pathways to Pain Relief: Insights and Resources for Your Journey
Hypopressives Are Not About “Reducing Pressure”
For years, Hypopressives have been explained as a way to reduce intra-abdominal pressure. But newer research suggests that story is too simplistic. In this article, I explore why the pressure-reduction narrative is outdated, what the latest study actually found, and why pelvic floor symptoms need to be understood through the whole body, including posture, breath, fascia, nervous system state, old injuries, compensation patterns and lived experience.
The Silent Signs of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Most Women Ignore
Many women sense that something isn’t quite right long before they actually pinpoint what it is. The most obvious things we notice are a heaviness as the day goes on that wasn’t there in the morning, a need to sit down sooner than you used to. A subtle checking-in with your body before you cough, laugh, lift or jump.
These early signs of pelvic floor dysfunction rarely feel at all dramatic. They feel vague, you make small adjustments, it is manageable and to easy to dismiss.
Signs of a Strong Pelvic Floor: How Real Pelvic Floor Recovery Shows Up
If you are looking for the signs of a strong pelvic floor, you are probably waiting for something obvious.
No leaking when you move, no damp pants after a dog walk, no heaviness in the middle or end of the day. No strange sensations, like a tampon being stuck or bubbles as you move, or your lower back not hurting anymore.
But pelvic floor recovery rarely arrives with fireworks. It arrives gradually and quietly, like a ninja.
Endometriosis, Pressure and the Breath
Endometriosis is not simply a reproductive condition. It is a whole-body inflammatory and neurological experience.
It is defined by the presence of endometrium-like tissue outside the uterus, most commonly on the ovaries, uterosacral ligaments, pelvic peritoneum and bowel. In some cases it is also found on the diaphragm. Research has consistently shown that it is associated with chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, painful defecation, bladder symptoms and fatigue. The European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology and multiple systematic reviews describe endometriosis as a chronic inflammatory condition with both peripheral and central sensitisation components.
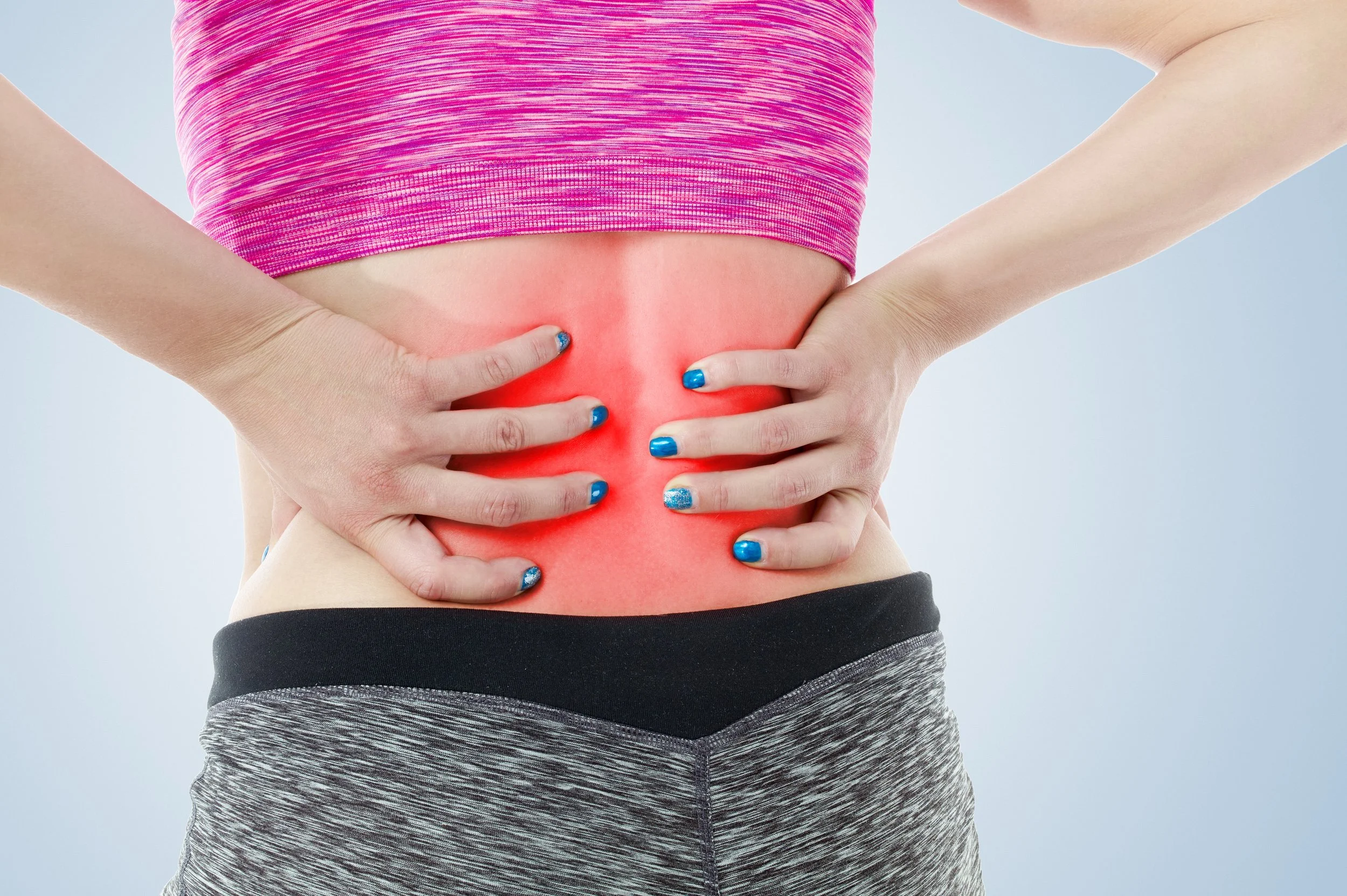
Lower Back Pain and Core Weakness: Can Hypopressives Help You Move Pain-Free?
If you’ve been dealing with lower back pain for a long time, you may already be doing “all the right things.” You exercise, you stretch, you stretch some more, you try to sit up straight (even writing that phrase makes me wince a little), and you’re told to strengthen your core (this is a phrase that is bandied around, but what does it actually mean? sit ups? Planks?).
Yet the pain keeps coming back, or never actually goes away.
In my studio, I see this every week. Women who are strong, capable and active, but who feel unstable through the middle or tight across the lower back. They are not lazy. They are not weak. They are often overworking.
Persistent back pain is rarely about effort or motivation. Very often, it is about how your body is coordinating breath, pressure and support.
This is where hypopressive exercises offer a different, and often relieving, perspective.
Internal Rectal Intussusception, Rectal Pressure & Prolapse
The puborectalis must lengthen at the right moment.
The pelvic floor must soften, not brace.
The diaphragm must move so pressure distributes evenly rather than travelling downward.
When those pieces work together, the system feels lighter. More efficient. Less effortful.
When they do not, symptoms like rectal pressure, incomplete emptying, and heaviness can appear — even when imaging findings are mild.
This is why the conversation around internal rectal intussusception, posterior prolapse, and outlet symptoms cannot stop at the scan report. The scan tells us what the tissue did during a test. It does not tell us how well your pressure system adapts day to day.
From Fight or Flight to Flow: Calming the Nervous System to Heal Your Pelvic Floor
You were never meant to live in a constant state of alert, modern life has had a huge impact on this, keeping us in a constant state of low level fear and anxiety. When the body finally feels safe, breath deepens, tension softens and healing becomes possible. Finding calm and space for you is not weakness or you being less productive. It is about you filling your cup and making space for your body to feel safe enough to let go so that it can build strength.
Your pelvic floor does not need more force. It needs safety, patience and permission from your nervous system to return to flow.
When Motivation Isn’t the Problem
When the goal feels endless, invisible, or too big, the dopamine level drops. The system starts to disengage.
If you are trying to be productive in every area of your life all at once or all at the same time, health, parenting, work, fitness, relationships then your reward circuitry becomes diluted. There are too many open loops. Too much effort without any closure. The brain doesn’t interpret that as strength. It reads it as overload.
The Mind–Pelvis Connection: How Emotions, Trauma and Stress Affect Pelvic Floor Health
Many people experience pelvic floor symptoms without any clear injury, diagnosis or structural explanation. These can appear as tightness, pain, leaking, heaviness or even a feeling of gripping or just feeling disconnected.
Scans and tests often come back “normal”, yet the symptoms persist. This can be deeply frustrating and confusing, especially when you believe you are doing all the “right” things.
Increasingly, research and clinical experience are highlighting the mind–body pelvic floor connection. The pelvis is not just a set of muscles. It is part of a complex system shaped by emotions, stress, trauma, breath and the nervous system.
Can Hypopressives Help with Prolapse? Natural Support for Bladder, Uterus & Bowel Health
If you are living with prolapse symptoms, you are not weak, failing, or broken. You are one of many women navigating changes in the body that are far more common than most of us were ever told.
Bladder, uterine and bowel prolapse affect a significant number of women, particularly after pregnancy and birth, and again during peri-menopause and menopause. Many describe a feeling of heaviness, dragging, pressure or a bulge. Others notice leaking, discomfort with exercise, or a sense that their body no longer feels supportive or reliable.
The Femoral Cutaneous Nerve: The Overlooked Nerve That Can Mimic Pelvic, Hip & Thigh Pain
Femoral cutaneous nerve irritation doesn’t feel like a pulled muscle.
Women often describe: Burning or heat across the thigh, tingling or pins and needles, numb patches, a buzzing or electric quality, pain that worsens with standing, walking or tight clothing
And crucially: It may ease when sitting or lying, stretching the thigh often doesn’t help, strength work can make it worse
Pelvic Floor Restoration vs Pelvic Floor Management: What’s the Difference?
Why pelvic floor restoration is different
Pelvic floor restoration is not about doing more.
It’s about changing the relationship you have with your body.
Restoration focuses on:
helping the body feel safe again
reducing nervous system vigilance
restoring natural coordination between breath, pressure, and support
rebuilding confidence through gradual, real-life movement
Rather than asking you to control your body, restoration helps your body relearn how to support you.
The goal isn’t perfection.
The goal is trust.
Training with Hypermobility & hEDS: Why “Being Flexible” Isn’t the Problem
What’s really going on in a hypermobile body?
With hEDS, the connective tissue that usually provides passive joint support is more elastic. That means the body has to rely much more on:
Muscle timing
Nervous system responses
Proprioception (your sense of where you are in space)
So instead of feeling solid and predictable, the body can feel:
Floaty or unstable
Over-alert
Or paradoxically… very tight
That tightness isn’t strength — it’s protection.
Many hypermobile people are both bendy and braced at the same time.
5 Things You Can Do Today to Help Your Pelvic Floor
Most women I work with haven’t done “nothing”.
They’ve done too much, in the wrong order.
So here are five things you can do today that actually support your pelvic floor — not by forcing it to behave, but by giving it the conditions it needs to respond.
Pelvic Floor Myths vs Reality: Why “Just Do Your Kegels” Often Isn’t the Answer
If I Make My Pelvic Floor Tighter, I’ll Be Stronger
This is one of the most common misunderstandings — and one of the most damaging.
Tightness feels like control.
It feels like effort.
It feels like you’re doing something.
But tight isn’t the same as strong.
A muscle that’s always gripping is often tired, under-oxygenated, and struggling to respond when it actually needs to. Many people with pelvic floor symptoms are already holding — through their belly, jaw, shoulders, glutes, breath — without even realising it.
Breath Holds, Vacuums & the Pelvic Floor
Healing and training the pelvic floor is not about choosing one method.
It’s about sequence.
Just as a personal trainer wouldn’t load strength onto a stiff, guarded body, we don’t ask the pelvic floor to “work harder” before it knows how to release, move, coordinate and recover.
TRE® helps reduce chronic tension and trauma-driven guarding, restoring a baseline sense of safety in the nervous system.
Hypopressives then restore posture, breath timing, pressure management and fascial expandability — allowing an internal lift through passive recoil, organ repositioning and reflexive pelvic floor response. This is mobility and coordination training for the pelvic floor, supported by intermittent hypoxia and cellular adaptation.
Only then do we layer in Pelvic Floor Muscle Training (PFMT) — the strength work that builds urethral and vaginal closure, resting tone and endurance.
Just as strength training without mobility creates stiff, non-functional “gym strong” bodies, pelvic floor strength without mobility and coordination fails to solve pressure problems.
The Vagus Nerve, the Heart, the Diaphragm
You may have heard the vagus nerve described as the calming nerve , or been told to “stimulate it” with breathing exercises, humming, or slow exhales.
That idea isn’t wrong.
But it’s incomplete.
The vagus nerve isn’t a switch you turn on. It’s part of a communication network linking your brain, heart, breath, diaphragm, gut , and indirectly, your pelvic floor.
Understanding this network helps explain why breath, posture, pressure, and nervous-system awareness matter so much in pelvic health.